生成式模型擅长解决许多类型的问题。不过,它们会受到以下限制:
- 模型在训练后被冻结,导致知识过时。
- 无法查询或修改外部数据。
函数调用可以帮助您克服其中的一些限制。 函数调用有时也称为“工具使用”,因为它允许模型使用外部工具(例如 API 和函数)来生成最终回答。
本指南将向您展示如何实现类似于本页下一主要部分中所述场景的函数调用设置。概括来讲,在应用中设置函数调用的步骤如下:
第 1 步:编写一个函数,该函数可以向模型提供生成最终响应所需的信息(例如,该函数可以调用外部 API)。
第 2 步:创建描述函数及其参数的函数声明。
第 3 步:在模型初始化期间提供函数声明,以便模型知道在需要时如何使用该函数。
第 4 步:设置应用,以便模型可以发送所需信息,供应用调用函数。
第 5 步:将函数的响应传递回模型,以便模型生成最终响应。
函数调用示例概览
向模型发送请求时,您还可以向模型提供一组“工具”(例如函数),以便模型可以使用这些工具来生成最终回答。为了利用这些函数并调用它们(“函数调用”),模型和应用需要相互传递信息,因此建议通过多轮对话界面使用函数调用。
假设您有一个应用,用户可以在其中输入如下提示:What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?。
Gemini 模型可能不知道此天气信息;不过,假设您知道某个外部天气服务 API 可以提供此信息。您可以使用函数调用为 Gemini 模型提供访问该 API 及其天气信息的途径。
首先,您需要在应用中编写一个与此假设的外部 API 互动的函数 fetchWeather,该函数具有以下输入和输出:
| 参数 | 类型 | 必需 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 输入 | |||
location |
对象 | 是 | 要获取天气信息的城市及其所在州的名称。 仅支持美国境内的城市。必须始终是 city 和 state 的嵌套对象。
|
date |
字符串 | 是 | 要获取天气信息的日期(必须始终采用 YYYY-MM-DD 格式)。
|
| 输出 | |||
temperature |
整数 | 是 | 温度(华氏度) |
chancePrecipitation |
字符串 | 是 | 降水概率(以百分比表示) |
cloudConditions |
字符串 | 是 | 云状况(clear、partlyCloudy、mostlyCloudy、cloudy 之一)
|
在初始化模型时,您需要告知模型存在此 fetchWeather 函数,以及该函数在需要时如何用于处理传入的请求。这称为“函数声明”。模型不会直接调用函数。相反,当模型处理传入的请求时,会决定 fetchWeather 函数是否可以帮助其响应请求。如果模型认为该函数确实有用,则会生成结构化数据,以帮助您的应用调用该函数。
再次查看传入的请求:What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?。模型可能会决定 fetchWeather 函数可以帮助其生成回答。模型会查看 fetchWeather 需要哪些输入参数,然后为该函数生成大致如下所示的结构化输入数据:
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
模型会将此结构化输入数据传递给您的应用,以便您的应用可以调用 fetchWeather 函数。当应用从 API 收到天气状况后,会将信息传递给模型。有了这些天气信息,模型就可以完成最终处理,并针对 What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? 的初始请求生成回答
模型可能会提供如下最终自然语言回答:On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
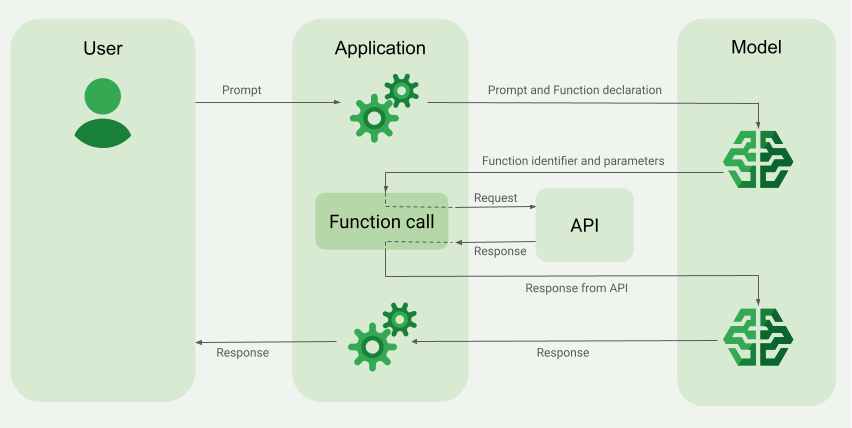
实现函数调用
本指南中的以下步骤将向您展示如何实现与函数调用示例概览(请参阅本页面的顶部部分)中所述工作流程类似的函数调用设置。
准备工作
|
点击您的 Gemini API 提供商,以查看此页面上特定于提供商的内容和代码。 |
如果您尚未完成入门指南,请先完成该指南。该指南介绍了如何设置 Firebase 项目、将应用连接到 Firebase、添加 SDK、为所选的 Gemini API 提供程序初始化后端服务,以及创建 GenerativeModel 实例。
如需测试和迭代提示,我们建议使用 Google AI Studio。
第 1 步:编写函数
假设您有一个应用,用户可以在其中输入如下提示:What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?。Gemini 模型可能不知道此天气信息;不过,假设您知道某个外部天气服务 API 可以提供此信息。本指南中的场景依赖于此假设的外部 API。
在应用中编写将与假设的外部 API 互动的函数,并向模型提供生成最终请求所需的信息。在此天气示例中,fetchWeather 函数将调用此假设的外部 API。
Swift
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
Unity
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
第 2 步:创建函数声明
创建您稍后将提供给模型的函数声明(本指南的下一步)。
在声明中,请尽可能详细地说明函数及其参数。
模型会使用函数声明中的信息来确定要选择哪个函数,以及如何为实际的函数调用提供形参值。如需了解模型如何选择函数以及如何控制该选择,请参阅本页稍后的其他行为和选项。
请注意,您提供的架构应满足以下条件:
您必须以与 OpenAPI 架构兼容的架构格式提供函数声明。 Vertex AI 对 OpenAPI 架构提供有限支持。
支持以下属性:
type、nullable、required、format、description、properties、items、enum。不支持以下属性:
default、optional、maximum、oneOf。
默认情况下,对于 Firebase AI Logic SDK,除非您在
optionalProperties数组中将所有字段指定为可选,否则所有字段都被视为必填。对于这些可选字段,模型可以填充字段或跳过字段。请注意,如果您使用这两个Gemini API提供商的服务器 SDK 或直接使用其 API,则此行为与默认行为相反。
如需了解与函数声明相关的最佳实践(包括有关名称和说明的提示),请参阅 Google Cloud 文档中的 Gemini Developer API 文档中的最佳实践。
您可以按以下方式编写函数声明:
Swift
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
Unity
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
第 3 步:在模型初始化期间提供函数声明
您可以在请求中提供的函数声明的最大数量为 128 个。如需了解模型如何选择函数,以及如何控制该选择(使用 toolConfig 设置函数调用模式),请参阅本页稍后的其他行为和选项。
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
了解如何选择适合您的应用场景和应用的模型 。
第 4 步:调用函数以调用外部 API
如果模型确定 fetchWeather 函数确实可以帮助其生成最终响应,则您的应用需要使用模型提供的结构化输入数据实际调用该函数。
由于需要在模型和应用之间来回传递信息,因此建议通过多轮对话界面使用函数调用。
以下代码段展示了如何告知应用模型想要使用 fetchWeather 函数。它还显示,模型已为函数调用(及其底层外部 API)提供了必要的输入参数值。
在此示例中,传入的请求包含提示 What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?。从这个提示中,模型推断出 fetchWeather 函数所需的输入参数(即 city、state 和 date)。
Swift
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
Unity
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
第 5 步:向模型提供函数的输出,以生成最终回答
在 fetchWeather 函数返回天气信息后,您的应用需要将其传递回模型。
然后,模型会执行最终处理,并生成最终的自然语言回答,例如:
On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Swift
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
Unity
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
其他行为和选项
以下是函数调用的一些其他行为,您需要在代码中适应这些行为,并可控制一些选项。
模型可能会要求再次调用某个函数或调用另一个函数。
如果一次函数调用的响应不足以让模型生成最终响应,那么模型可能会要求进行额外的函数调用,或者要求调用完全不同的函数。只有当您在函数声明列表中向模型提供多个函数时,才会出现后一种情况。
您的应用需要适应模型可能会要求进行额外的函数调用。
模型可能会要求同时调用多个函数。
您可以在函数声明列表中向模型提供最多 128 个函数。鉴于此,模型可能会决定需要多个函数来帮助其生成最终回答。并且,它可能会决定同时调用其中的一些函数,这称为并行函数调用。
您的应用需要适应模型可能会要求同时运行多个函数的情况,并且需要将所有函数的响应提供给模型。
您可以控制模型是否可以请求调用函数以及调用方式。
您可以对模型应如何以及是否使用提供的函数声明进行一些限制。这称为设置函数调用模式。下面是一些示例:
您可以强制模型始终使用函数调用,而不是允许模型在立即生成自然语言回答和函数调用之间进行选择。这称为“强制函数调用”。
如果您提供多个函数声明,可以将模型限制为仅使用所提供函数的一部分。
您可以通过添加工具配置 (toolConfig) 以及提示和函数声明来实现这些约束条件(或模式)。在工具配置中,您可以指定以下模式之一。最实用的模式是 ANY。
| Mode | 说明 |
|---|---|
AUTO |
默认模型行为。模型决定是使用函数调用还是自然语言回答。 |
ANY |
模型必须使用函数调用(“强制函数调用”)。如需将模型限制为部分函数,请在 allowedFunctionNames 中指定允许使用的函数名称。
|
NONE |
模型不得使用函数调用。这种行为等同于模型请求没有任何关联的函数声明。 |
您还可以做些什么?
试用其他功能
了解如何控制内容生成
- 了解提示设计,包括最佳实践、策略和示例提示。
- 配置模型参数,例如温度和输出 token 数上限(对于 Gemini)或宽高比和人物生成(对于 Imagen)。
- 使用安全设置来调整获得可能被视为有害的回答的可能性。
详细了解支持的型号
了解适用于各种应用场景的模型及其配额和价格。就您使用 Firebase AI Logic 的体验提供反馈

