请阅读本指南,了解 Cloud Firestore Security Rules配置中的常见漏洞,检查并更好地保护您自己的规则,并在部署之前先测试更改。
如果您收到有关 Cloud Firestore 数据库未得到适当保护的提醒,可以通过修改和测试 Cloud Firestore Security Rules 来消除这些漏洞。
如需查看您现有的安全规则,请前往 Firebase 控制台中的“规则”标签页。
了解您的 Cloud Firestore Security Rules
Cloud Firestore Security Rules可保护您的数据免受恶意用户的攻击。Firebase 控制台中创建的任何 Cloud Firestore 实例的默认规则都拒绝所有用户访问。要开发应用并访问数据库,您需要修改这些规则,并可以考虑为开发环境中所有用户授予完整访问权限。但是,在将应用部署到生产环境之前,请花些时间正确配置您的规则并保护您的数据。
在开发应用并测试规则的不同配置时,请使用 Cloud Firestore 模拟器在本地开发环境中运行应用。
具有不安全规则的常见场景
您可能已经设置了默认的 Cloud Firestore Security Rules,或者在刚开始使用 Cloud Firestore 开发应用时设置了规则,但在部署应用之前,您应该检查并更新这些规则。确保避免以下常见误区,从而妥善保护用户数据的安全。
允许所有人访问
在开发期间,您在设置 Cloud Firestore 时可能已将规则设置为允许所有人访问。您可能认为只有您在使用自己的应用,但如果您已经部署了该应用,互联网用户就都可以使用。如果您未对用户进行身份验证并配置安全规则,则猜测出您的项目 ID 的任何人都可以窃取、篡改或删除数据。
| 不推荐:对所有用户授予读写权限。 |
// Allow read/write access to all users under any conditions // Warning: **NEVER** use this rule set in production; it allows // anyone to overwrite your entire database. service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { match /{document=**} { allow read, write: if true; } } }
|
解决方法:使用规则限制读写权限。
构建适合您的数据层次结构的规则。针对这种危险因素的一种常见解决方案是,使用 Firebase Authentication 实现基于用户的安全控制。详细了解如何使用规则对用户进行身份验证。 |
仅限内容所有者
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Allow only authenticated content owners access match /some_collection/{document} { // Allow reads and deletion if the current user owns the existing document allow read, delete: if request.auth.uid == resource.data.author_uid; // Allow creation if the current user owns the new document allow create: if request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.author_uid; // Allow updates by the owner, and prevent change of ownership allow update: if request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.author_uid && request.auth.uid == resource.data.author_uid; } } }
既提供公共访问权限,又提供专属访问权限
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Allow public read access, but only content owners can write match /some_collection/{document} { // Allow public reads allow read: if true // Allow creation if the current user owns the new document allow create: if request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.author_uid; // Allow updates by the owner, and prevent change of ownership allow update: if request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.author_uid && request.auth.uid == resource.data.author_uid; // Allow deletion if the current user owns the existing document allow delete: if request.auth.uid == resource.data.author_uid; } } }
为通过身份验证的用户提供访问权限
有时,Cloud Firestore Security Rules会检查用户是否已登录,但不会再通过身份验证进一步限制访问权限。如果您的某一条规则包含 auth != null,请确认您是否想让所有已登录的用户有权访问数据。
| 不推荐:任何登录用户都有权在您的整个数据库中读写数据。 |
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { match /some_collection/{document} { allow read, write: if request.auth != null; } } }
| 解决方案:使用安全条件缩小访问权限范围。
在验证身份时,您可以使用某个身份验证属性来进一步限制特定用户对特定数据集的访问权限。详细了解添加安全条件和基于角色的访问权限。 |
基于角色的访问权限
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Assign roles to all users and refine access based on user roles match /some_collection/{document} { allow read: if request.auth != null && get(/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(request.auth.uid)).data.role == "Reader" allow write: if request.auth != null && get(/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(request.auth.uid)).data.role == "Writer" // Note: Checking for roles in your database using `get` (as in the code // above) or `exists` carry standard charges for read operations. } } }
基于属性的访问权限
// Give each user in your database a particular attribute // and set it to true/false // Then, use that attribute to grant access to subsets of data // For example, an "admin" attribute set // to "true" grants write access to data service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { match /collection/{document} { allow write: if get(/databases/$(database)/documents/users/$(request.auth.uid)).data.admin == true; allow read: true; } } }
既提供公共访问权限,又提供专属访问权限
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
// Allow public read access, but only content owners can write
match /some_collection/{document} {
allow read: if true
allow write: if request.auth.uid == request.resource.data.author_uid
}
}
}
未验证的电子邮件地址的访问权限
有时,Cloud Firestore Security Rules 会检查用户的电子邮件地址是否属于特定网域。虽然这通常是一种很好的做法,但在登录时并不总是会验证电子邮件,而是在用户收到验证电子邮件后执行额外步骤时进行验证。确保您验证该电子邮件确实属于该用户。
| 不推荐:任何用户都可以使用任意电子邮件地址登录。 |
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Allow access based on email domain match /some_collection/{document} { allow read: if request.auth != null && request.auth.email.endsWith('@example.com') } } }
| 解决方案:仅限已验证的电子邮件的访问权限。 |
验证电子邮件地址
service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Allow access based on email domain match /some_collection/{document} { allow read: if request.auth != null && request.auth.email_verified && request.auth.email.endsWith('@example.com') } } }
关闭访问权限
在开发应用时,另一种常见方法是封锁数据。通常,这意味着您已关闭所有用户的读写权限,如下所示:
// Deny read/write access to all users under any conditions
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
match /{document=**} {
allow read, write: if false;
}
}
}
Firebase Admin SDK 和 Cloud Functions 仍可以访问您的数据库。如果您打算将 Cloud Firestoree 作为仅限服务器的后端与 Firebase Admin SDK 结合使用,请使用这些规则。虽然这种做法是安全的,但您应该测试应用的客户端是否可以正确检索数据。
如需详细了解 Cloud Firestore Security Rules 及其工作原理,请参阅 Cloud Firestore Security Rules使用入门。
查看 Cloud Firestore Security Rules
如需检查应用的行为并验证您的 Cloud Firestore Security Rules配置,请使用 Cloud Firestore 模拟器。先使用 Cloud Firestore 模拟器在本地环境中运行单元测试并使之自动化,然后再部署更改。
如需在 Firebase 控制台中快速测试更新后的 Cloud Firestore Security Rules,请使用“规则测试平台”工具。
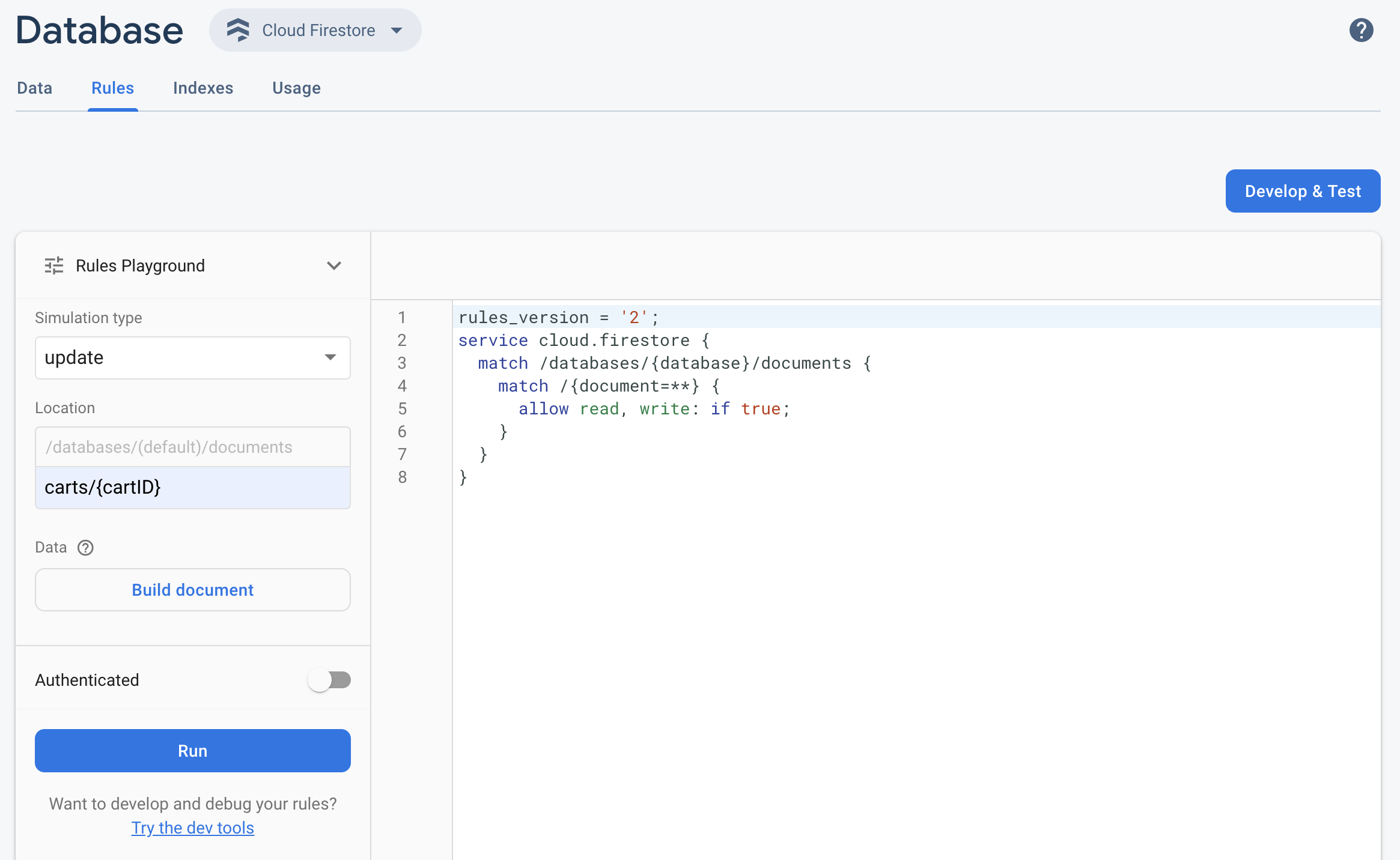
- 如需打开规则测试平台,请点击“规则”标签页中的规则测试平台。
- 在“规则测试平台”设置中,选择用于测试的选项,包括:
- 测试读取或写入
- 数据库中的特定位置(以路径表示)
- 身份验证类型 - 未经身份验证、经过身份验证的匿名用户或特定用户 ID
- 您的规则特别引用的文档专属数据(例如,如果您的规则要求必须存在特定字段才允许执行写入操作)
- 点击运行,然后在规则窗口上方的横幅中查看结果。
